Lab 4
Introduction
The purpose of Lab 4 was to program an STM32 MCU to play a sequence of specified frequencies and durations. Currently, it is capable of playing excerpts from Fur Elise by Beethoven and Hopes and Dreams by Toby Fox.
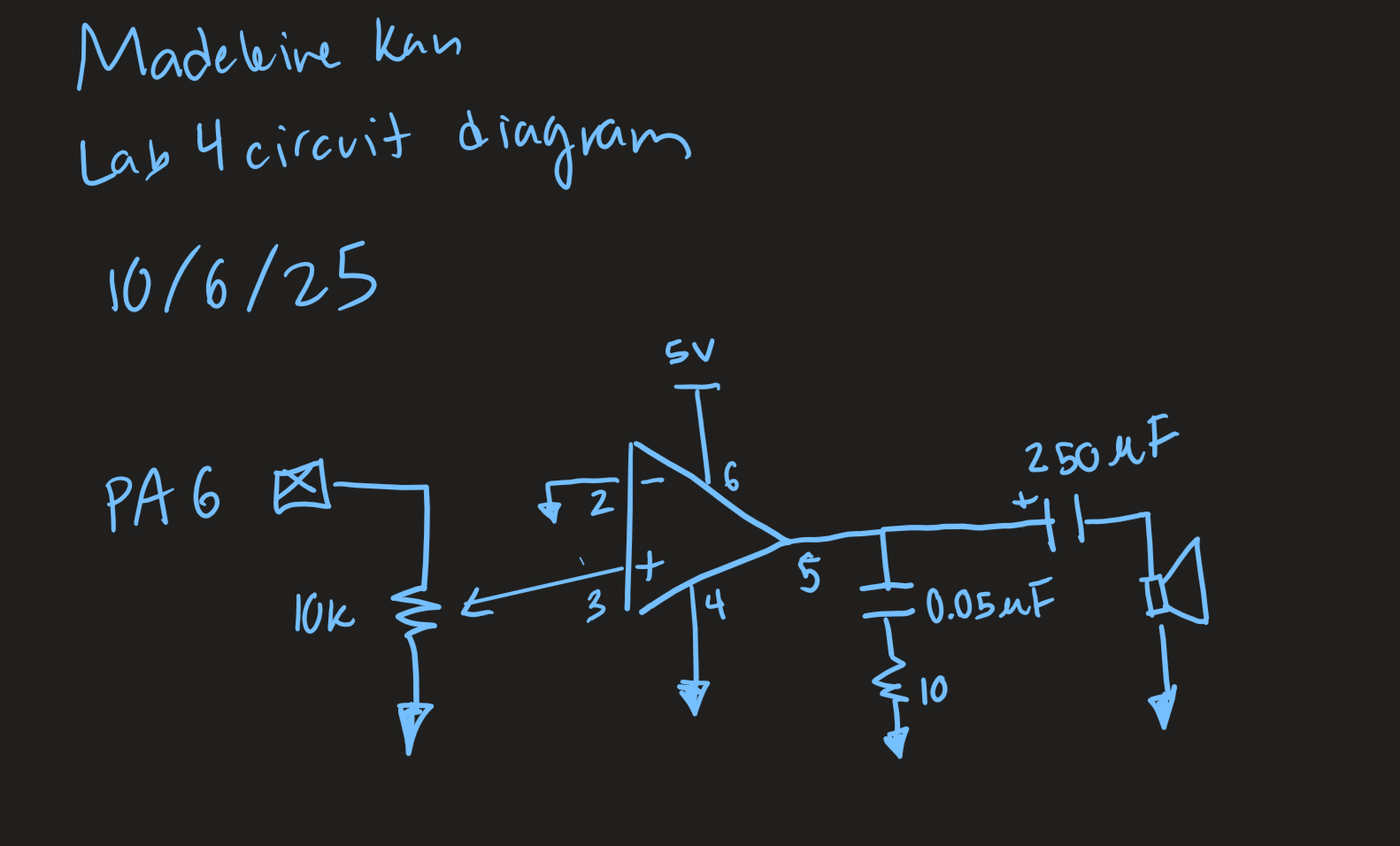
Schematic
The circuit diagram is as follows:
Calculations
Minimum and maximum duration and frequencies:

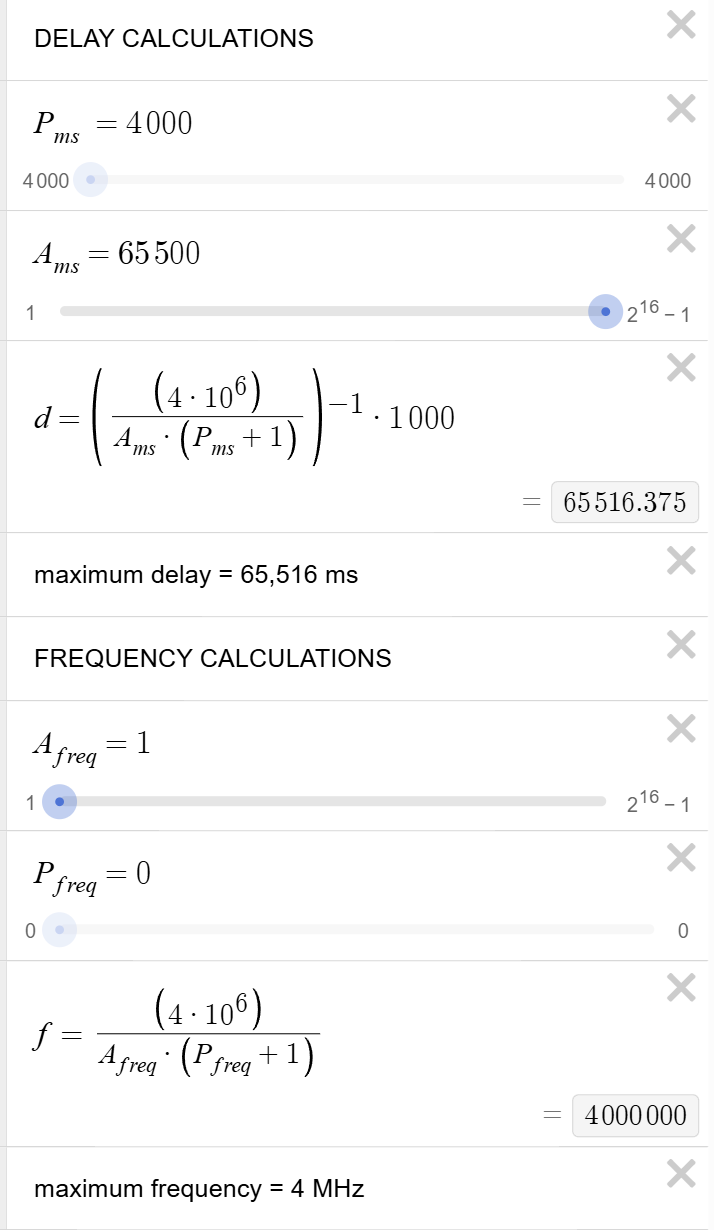
Frequency calculation for 220, 660, and 100 Hz (within 1% error):



Code:
Updated GPIO.h library header file:
// STM32L432KC_GPIO.h
// Header for GPIO functions
// Madeleine Kan
// mkan@hmc.edu
// 10/6/25
#ifndef STM32L4_GPIO_H
#define STM32L4_GPIO_H
#include <stdint.h> // Include stdint header
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Definitions
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Values for GPIO pins ("val" arguments)
#define GPIO_LOW 0
#define GPIO_HIGH 1
// Base addresses for GPIO ports
#define GPIOB_BASE (0x48000400UL)
#define GPIOA_BASE (0x48000000UL)
// see button interrupt tutorial, pin A + more generality
// Arbitrary GPIO functions for pinMode()
#define GPIO_INPUT 0
#define GPIO_OUTPUT 1
#define GPIO_ALT 2
#define GPIO_ANALOG 3
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Bitfield struct for GPIO
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// GPIO register structs here
typedef struct {
volatile uint32_t MODER; // GPIO Offset 0x00 GPIO port mode register
volatile uint32_t OTYPER; // GPIO Offset 0x04
volatile uint32_t OSPEEDR; // GPIO Offset 0x08
volatile uint32_t PURPDR; // GPIO Offset 0x0C
volatile uint32_t IDR; // GPIO Offset 0x10
volatile uint32_t ODR; // GPIO Offset 0x14
volatile uint32_t BSRR; // GPIO Offset 0x18
volatile uint32_t LCKR; // GPIO Offset 0x1C
volatile uint32_t AFRL; // GPIO Offset 0x20
volatile uint32_t AFRH; // GPIO Offset 0x24
} GPIO;
// Pointers to GPIO-sized chunks of memory for each peripheral
#define GPIOB ((GPIO *) GPIOB_BASE)
#define GPIOA ((GPIO *) GPIOA_BASE)
#define GPIO GPIOA
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Function prototypes
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void pinMode(int pin, int function);
int digitalRead(int pin);
void digitalWrite(int pin, int val);
void togglePin(int pin);
#endifUpdated RCC.c library file:
// STM32L432KC_RCC.c
// Source code for RCC functions
// Madeleine Kan
// mkan@hmc.edu
// 10/6/25
#include "STM32L432KC_RCC.h"
void configureClock(){
// MSI is automatically set as systemclock
RCC->APB2ENR |= (1 << 17); // tim16 timer clk enable
RCC->APB2ENR |= (1 << 16); // tim15 timer clk enable
}New TIMER.c library file:
// TIMER.c
// Source code for Timer functions (delay and output 50% PWM at desired frequency)
// Madeleine Kan
// mkan@hmc.edu
// 10/6/25
#include "STM32L432KC_TIMER.h"
void configureTimer(TIM_TypeDef* TIMx, int PWM) {
if (PWM == 1) {
TIMx->CCMR1 |= (0b110 << 4); // set PWM mode 1 (active high)
TIMx->CCMR1 |= (1 << 3); // output compare 1 preload enable
TIMx->BDTR |= (1 << 15); // main output enable
// TIMx->CCER |= (1 << 1); // CC1E, enable OC1 signal
TIMx->CCER |= (1 << 0); // CC1E, enable OC1 signal
}
// preload value copied into active capture/compare register when update event occurs
// update generation... cleared by hardware, care of enable and disabling counter
TIMx->EGR |= (1 << 0); // reinitialize counter, generate update of registers
// enable counter
TIMx->CR1 |= (1 << 0); // write 1 to CEN
// set URS to overflow/underflow only ... maybe relevant for upcout nmode?
// TIMx->CR1 |= (1 << 2);
}
// output PWM signal at desired frequency
void setTimerFreq(TIM_TypeDef* TIMx, uint16_t freq, uint16_t prescale_val) {
// (4 MHz) / (prescaler_val * auto_reload_val)
// must span 220-1000 Hz with 1% accuracy
//uint16_t prescale_val;
uint16_t auto_reload_val;
if (freq > 0) {
auto_reload_val = 4000000 / freq;
} else {
auto_reload_val = 0;
}
uint16_t duty_cycle = auto_reload_val / 2;
//// clear counter
//TIMx->CNT &= ~(0b1111111111111111 << 0);
// wite ARR
TIMx->ARR &= ~(0b1111111111111111 << 0); // clear ARR
TIMx->ARR |= (auto_reload_val << 0); // set ARR
// counter clock frequency (CK_CNT) = f_CKPSC / (PSC[15:0] + 1)
TIMx->PSC |= (prescale_val << 0); // set psc3q
// value is compared to timx_cnt, signaled on oc1 output
TIMx->CCR1 &= ~(0b1111111111111111 << 0); // clear CCR1
TIMx->CCR1 |= (duty_cycle << 0); // set PWM count
// update generation... cleared by hardware, care of enable and disabling counter
TIMx->EGR |= (1 << 0); // reinitialize counter, generate update of registers
// clear counter
TIMx->CNT &= ~(0b1111111111111111 << 0);
}
// delay for speceified number of milliseconds
void delay_millis(TIM_TypeDef* TIMx, uint16_t ms, uint16_t prescale_val) {
// (4 MHz) / (prescaler_val * auto_reload_val)
// must span 220-1000 Hz with 1% accuracy
uint16_t auto_reload_val;
auto_reload_val = ms;
// wite ARR
TIMx->ARR &= ~(0b1111111111111111 << 0); // clear ARR
TIMx->ARR |= (auto_reload_val << 0); // set ARR
// counter clock frequency (CK_CNT) = f_CKPSC / (PSC[15:0] + 1)
TIMx->PSC |= (prescale_val << 0); // set psc3q
// update generation... cleared by hardware, care of enable and disabling counter
TIMx->EGR |= (1 << 0); // reinitialize counter, generate update of registers
TIMx->SR &= ~(1 >> 0); // reset duration UIF
// clear counter
TIMx->CNT &= ~(0b1111111111111111 << 0);
while ((TIMx->SR >> 0 & 1) != 1); // wait for UIF to be 1
TIMx->SR &= ~(1 >> 0); // reset duration UIF
}New TIMER.h library header file
// TIMER.h
// Header for TIMER functions
#ifndef STM32L4_TIMER_H
#define STM32L4_TIMER_H
#include <stdint.h>
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Definitions
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#define __IO volatile
// Base addresses... programmers manual p60
#define TIM15_BASE (0x40014000UL) // base address of TIM15
#define TIM16_BASE (0x40014400UL) // base address of TIM16
/**
* @brief Reset and Clock Control
*/
typedef struct
{
__IO uint32_t CR1; /*!< TIM control register 1, Address offset: 0x00 */
__IO uint32_t CR2; /*!< TIM control register 2, Address offset: 0x04 */
__IO uint32_t SMCR; /*!< TIM slave mode control register, Address offset: 0x08 */
__IO uint32_t DIER; /*!< TIM DMA/interrupt enable register, Address offset: 0x0C */
__IO uint32_t SR; /*!< TIM status register, Address offset: 0x10 */
__IO uint32_t EGR; /*!< TIM event generation register, Address offset: 0x14 */
__IO uint32_t CCMR1; /*!< TIM capture/compare mode register 1, Address offset: 0x18 */
__IO uint32_t CCMR2; /*!< TIM capture/compare mode register 2, Address offset: 0x1C */
__IO uint32_t CCER; /*!< TIM capture/compare enable register, Address offset: 0x20 */
__IO uint32_t CNT; /*!< TIM counter register, Address offset: 0x24 */
__IO uint32_t PSC; /*!< TIM prescaler, Address offset: 0x28 */
__IO uint32_t ARR; /*!< TIM auto-reload register, Address offset: 0x2C */
__IO uint32_t RCR; /*!< TIM repetition counter register, Address offset: 0x30 */
__IO uint32_t CCR1; /*!< TIM capture/compare register 1, Address offset: 0x34 */
__IO uint32_t CCR2; /*!< TIM capture/compare register 2, Address offset: 0x38 */
__IO uint32_t CCR3; /*!< TIM capture/compare register 3, Address offset: 0x3C */
__IO uint32_t CCR4; /*!< TIM capture/compare register 4, Address offset: 0x40 */
__IO uint32_t BDTR; /*!< TIM break and dead-time register, Address offset: 0x44 */
__IO uint32_t DCR; /*!< TIM DMA control register, Address offset: 0x48 */
__IO uint32_t DMAR; /*!< TIM DMA address for full transfer, Address offset: 0x4C */
__IO uint32_t OR1; /*!< TIM option register 1, Address offset: 0x50 */
__IO uint32_t CCMR3; /*!< TIM capture/compare mode register 3, Address offset: 0x54 */
__IO uint32_t CCR5; /*!< TIM capture/compare register5, Address offset: 0x58 */
__IO uint32_t CCR6; /*!< TIM capture/compare register6, Address offset: 0x5C */
__IO uint32_t OR2; /*!< TIM option register 2, Address offset: 0x60 */
__IO uint32_t OR3; /*!< TIM option register 3, Address offset: 0x64 */
} TIM_TypeDef;
#define TIM15 ((TIM_TypeDef *)TIM15_BASE)
#define TIM16 ((TIM_TypeDef *)TIM16_BASE)
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Function prototypes
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void configureTimer(TIM_TypeDef * TIMx, int PWM);
void setTimerFreq(TIM_TypeDef * TIMx, uint16_t freq, uint16_t prescale_val);
void delay_millis(TIM_TypeDef * TIMx, uint16_t ms, uint16_t prescale_val);
#endifmain.c Source code:
/*********************************************************************
* SEGGER Microcontroller GmbH *
* The Embedded Experts *
**********************************************************************
-------------------------- END-OF-HEADER -----------------------------
File : main.c
Purpose : Play specified song
Madeleiene Kan
mkan@hmc.edu
10/6/25
*/
// Includes for libraries
#include "C:\Users\mkan\Documents\GitHub\e155-lab4\lib\STM32L432KC_FLASH.h"
#include "C:\Users\mkan\Documents\GitHub\e155-lab4\lib\STM32L432KC_RCC.h"
#include "C:\Users\mkan\Documents\GitHub\e155-lab4\lib\STM32L432KC_TIMER.h"
#include "C:\Users\mkan\Documents\GitHub\e155-lab4\lib\STM32L432KC_GPIO.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
// Define macros for constants
#define LED_PIN 6
#define DELAY_DURATION_MS 500
const int notes[][2] = {
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{494, 125},
{587, 125},
{523, 125},
{440, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{262, 125},
{330, 125},
{440, 125},
{494, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{416, 125},
{494, 125},
{523, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{494, 125},
{587, 125},
{523, 125},
{440, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{262, 125},
{330, 125},
{440, 125},
{494, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{523, 125},
{494, 125},
{440, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{494, 125},
{523, 125},
{587, 125},
{659, 375},
{392, 125},
{699, 125},
{659, 125},
{587, 375},
{349, 125},
{659, 125},
{587, 125},
{523, 375},
{330, 125},
{587, 125},
{523, 125},
{494, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{659, 125},
{ 0, 250},
{659, 125},
{1319, 125},
{ 0, 250},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{ 0, 250},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{494, 125},
{587, 125},
{523, 125},
{440, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{262, 125},
{330, 125},
{440, 125},
{494, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{416, 125},
{494, 125},
{523, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{623, 125},
{659, 125},
{494, 125},
{587, 125},
{523, 125},
{440, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{262, 125},
{330, 125},
{440, 125},
{494, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{330, 125},
{523, 125},
{494, 125},
{440, 500},
{ 0, 0}};
const int hopes[][2] = {
{349, 250}, // F4
{ 0, 125},
{698, 250}, // F5
{ 0, 125},
{523, 500}, // C4
{ 0, 125},
{466, 250}, // B4 flat
{ 0, 125},
{698, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{349, 500},
{ 0, 125},
{349, 250},
{ 0, 125},
{440, 250}, // A4
{ 0, 125},
{880, 375}, // A5
{ 0, 125},
{932, 125}, // B6 flat
{ 0, 125},
{880, 250}, // A5
{ 0, 125},
{698, 250}, // F5
{ 0, 125},
{1174, 63}, // D6
{ 0, 30},
{932, 63}, // B6 flat
{ 0, 30},
{880, 63},
{ 0, 30},
{698, 63}, //F5
{ 0, 30},
{587, 63}, //D5
{ 0, 30},
{523, 63}, //C5
{0, 0}
};
int main(void) {
configureFlash();
configureClock();
// Turn on clock to GPIOA
RCC->AHB2ENR |= (1 << 0);
pinMode(LED_PIN, GPIO_ALT);
GPIO->AFRL |= (0b1110 << 4*LED_PIN); // set alternate function for PA6 to AF14
// configure timers
uint16_t presc_freq = 0;
uint16_t presc_dur = 4000;
configureTimer(TIM15, 0); // upcount mode
configureTimer(TIM16, 1); // PWM mode
// Play Fur Elise
for (int i = 0; i<(sizeof(notes)/sizeof(notes[0])); i++) {
uint16_t freq = (uint16_t) notes[i][0];
uint16_t ms = (uint16_t) notes[i][1];
setTimerFreq(TIM16, freq, presc_freq);
delay_millis(TIM15, ms, presc_dur);
}
// Play Hopes and Dreams
for (int i = 0; i<(sizeof(hopes)/sizeof(hopes[0])); i++) {
uint16_t freq = (uint16_t) hopes[i][0];
uint16_t ms = (uint16_t) hopes[i][1];
setTimerFreq(TIM16, freq, presc_freq);
delay_millis(TIM15, ms, presc_dur);
}
return 0;
}- I asked copilot. The sample code it generated was helpful, but it didn’t cover the RCC config necessary to enable the timers and the GPIO pins. Also, I ended up ising Timer 16 and 17, which it did not cover. It seems clear that the AI can be informative, but it cannot read the datasheet. Here are the results:
To generate frequencies between 220 Hz and 1 kHz on the STM32L432KC and output them to a GPIO pin, here’s a complete breakdown of your best options and how to configure them:
---
### 🧠 Recommended Timers for Frequency Generation
The STM32L432KC features several timers, but for outputting waveforms to GPIO pins, **general-purpose timers** are ideal:
| Timer | Type | Output to GPIO | Channels | Notes |
|-------|-------------------|----------------|----------|-------|
| TIM2 | General-purpose | ✅ Yes | 4 | 32-bit counter, flexible |
| TIM5 | General-purpose | ✅ Yes | 4 | 32-bit counter, ideal for low frequencies |
| TIM1 | Advanced-control | ✅ Yes | 4 | More complex, used for PWM |
| TIM6/7| Basic timers | ❌ No | 0 | No direct GPIO output |
| LPTIM1| Low-power timer | ✅ Yes | 1 | Good for ultra-low-power apps |
🔧 **Best choice for GPIO output**: **TIM2 or TIM5**
These are general-purpose timers with multiple output channels and direct GPIO mapping via alternate function (AF) settings.
---
### 📐 Frequency Calculation Formula
To generate a specific frequency, use this formula:
f_timer = SystemCoreClock / ((PSC + 1) × (ARR + 1))
Where:
- `SystemCoreClock` is typically 80 MHz on STM32L432KC
- `PSC` = Prescaler value
- `ARR` = Auto-reload register value
You can fix one value (usually keep `PSC` low for better resolution) and solve for the other.
---
### 🛠️ Key Registers to Configure
To set up a timer for frequency output:
1. **Enable Timer Clock**
- RCC->APB1ENR |= RCC_APB1ENR_TIM2EN;
2. **Configure GPIO Pin for Alternate Function**
- Set GPIO mode to AF
- Choose correct AF (e.g., AF1 for TIM2_CH1 on PA0)
3. **Set Prescaler and ARR**
```c
TIM2->PSC = prescaler_value;
TIM2->ARR = auto_reload_value;Configure Output Compare Mode
TIM2->CCMR1 |= (6 << TIM_CCMR1_OC1M_Pos); // PWM mode 1 TIM2->CCER |= TIM_CCER_CC1E; // Enable output on CH1 TIM2->CCR1 = ARR / 2; // 50% duty cycleEnable Timer
TIM2->CR1 |= TIM_CR1_CEN;
🔌 GPIO Mapping Tips
To connect timer output to a GPIO pin: - Use the Alternate Function (AF) mapping in the datasheet. - Example: TIM2_CH1 is mapped to PA0 with AF1. - Configure the pin: c GPIOA->MODER &= ~(3 << (0 * 2)); GPIOA->MODER |= (2 << (0 * 2)); // Alternate function GPIOA->AFR[0] |= (1 << (0 * 4)); // AF1 for TIM2_CH1
🧮 Example: Generating 440 Hz with TIM2
Assuming SystemCoreClock = 80 MHz:
PSC = 181; // Prescaler
ARR = 999; // Auto-reload
f = 80e6 / ((181+1)*(999+1)) = ~440 HzWould you like help writing a full initialization function or configuring multiple frequencies dynamically?
```